Managing Side Effects of Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy, often referred to as “chemo,” is one of the leading treatments for different types of cancer, offering both hope and healing to millions of individuals around the world.
A regular aspect of modern oncology, chemotherapy includes the multiple drugs and treatment regimens that target and destroy cancer cells throughout the body.
While the mere mention of chemotherapy may trigger feelings of apprehension or uncertainty, it’s only wise to recognize the integral role it plays in the fight against cancer, offering the real possibility of remission and recovery for countless individuals affected by cancer.
In what follows, we describe the most common types of chemotherapy side effects and how they are managed effectively.
Common Side Effects of Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy, while a necessary treatment in the fight against cancer, often comes with a range of side effects that can impact patients both physically and emotionally.
These side effects vary from person to person and depend on factors such as the type of chemotherapy drugs used, the dosage, and individual differences in response. The following are the most common side effects of chemotherapy:
Physical Side Effects
Nausea and Vomiting: Nausea and vomiting are among the most well-known side effects of chemotherapy. Certain chemotherapy drugs can irritate the stomach lining and trigger the body’s vomiting reflex, leading to symptoms of nausea and episodes of vomiting.
Fatigue: Fatigue, or extreme tiredness, is another common side effect of chemotherapy. Chemotherapy drugs can affect the body’s ability to produce energy, leading to feelings of exhaustion and weakness that can persist throughout treatment.
Hair Loss: Many chemotherapy drugs target rapidly dividing cells, including those in the hair follicles, resulting in hair loss or thinning. Hair loss can be emotionally distressing for many patients, impacting self-image and confidence.
Mouth Sores: Chemotherapy can cause inflammation and ulceration of the mucous membranes lining the mouth, throat, and digestive tract, leading to painful mouth sores. Proper oral hygiene and mouth care are essential for preventing and managing mouth sores during treatment.
Loss of Appetite and Changes in Weight: Chemotherapy can affect appetite and taste perception, leading to a loss of appetite and changes in weight. Some patients may experience weight loss, while others may gain weight due to fluid retention or changes in metabolism.
Emotional/Cognitive Side Effects
Mood Changes: Chemotherapy can impact mood and emotional well-being, leading to feelings of anxiety, depression, or irritability. Coping with the physical and emotional challenges of treatment can take a toll on patients’ mental health.
Cognitive Impairment (Chemobrain): Chemotherapy-induced cognitive impairment, often referred to as “chemobrain,” is characterized by difficulties with memory, concentration, and multitasking. These cognitive changes can persist long after treatment has ended, impacting daily functioning and quality of life.
Stress: Managing the physical and emotional demands of chemotherapy treatment can be highly stressful for patients and their loved ones. Coping with the uncertainty of cancer diagnosis and treatment, along with potential side effects, can contribute to feelings of stress and overwhelm.
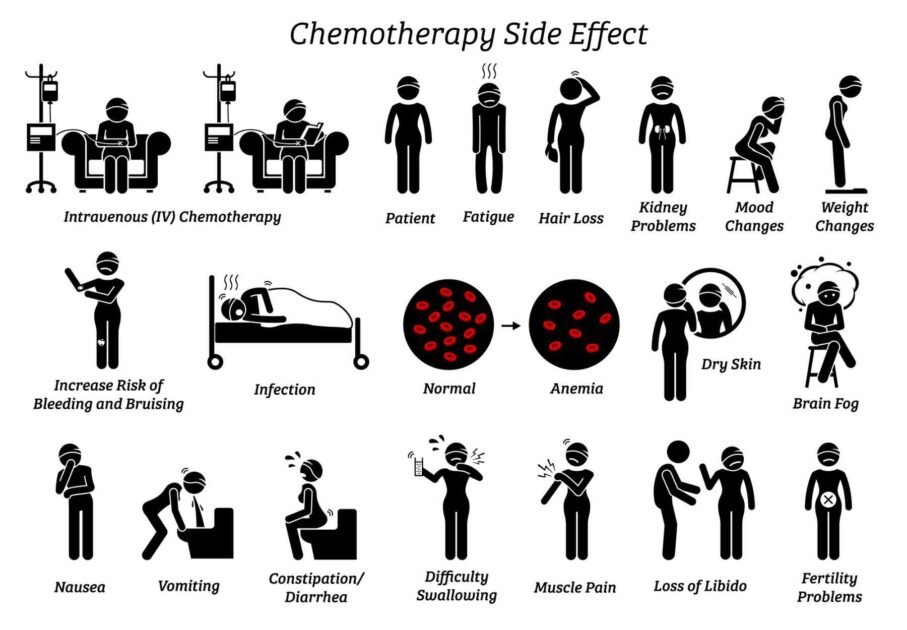
Managing Physical and Emotional Side Effects
Experiencing the physical and emotional side effects of chemotherapy can be challenging. Still, there are various strategies and interventions available to help patients cope with these difficulties and improve their overall quality of life during treatment.
Here are some effective approaches for managing both physical and emotional side effects:
Medication
Medications, such as antiemetics for nausea and vomiting and pain relievers for mouth sores or neuropathy, can help alleviate chemotherapy-related symptoms. Additionally, medications like antidepressants or anti-anxiety medications may be prescribed to manage mood changes and emotional distress.
Dietary Intervention
Making dietary modifications can help alleviate some chemotherapy side effects. For example, consuming small, frequent meals and avoiding spicy or greasy foods can help manage nausea and vomiting. Maintaining a balanced diet rich in protein, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can support overall health and energy levels during treatment.
Alternative Therapies
Complementary and alternative therapies, such as acupuncture, massage therapy, and relaxation techniques like meditation or yoga, can provide symptom relief and improve overall well-being. These therapies may help reduce stress, alleviate pain, and promote relaxation during chemotherapy treatment.
Coping Strategies
Engaging in coping strategies such as journaling, deep breathing exercises, and visualization techniques can help patients manage the emotional distress and anxiety associated with chemotherapy. Connecting with support groups or counseling services can also provide valuable emotional support and guidance throughout treatment.
Pain Management Techniques
Pain management techniques, including heat therapy, cold therapy, and transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS), can help alleviate chemotherapy-related pain and discomfort. Working closely with healthcare providers to develop a personalized pain management plan is essential for optimizing pain relief and improving quality of life.
Psychotherapy
Psychotherapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) or supportive therapy, can help patients cope with the emotional challenges of cancer diagnosis and treatment. By providing a safe space to talk about thoughts and feelings, psychotherapy can help patients develop effective coping strategies and improve their resilience during chemotherapy.
Supportive Care Services
Accessing supportive care services, such as palliative care or hospice care, can provide comprehensive support for patients and their families throughout the process. These services focus on managing symptoms, improving quality of life, and addressing practical needs.

Final Thoughts
Managing the physical and emotional side effects of chemotherapy requires a multifaceted approach that addresses both symptom management and emotional well-being.
By incorporating medication, dietary intervention, alternative therapies, coping strategies, pain management techniques, psychotherapy, and supportive care services into their treatment plan, patients can optimize their quality of life and better cope with the challenges of chemotherapy treatment.
Working closely with healthcare providers and support networks can provide valuable guidance and support throughout the treatment period.